Züs Cloud Storage Network Consensus Protocol
Züs (formerly) 0Chain recently released the latest of their protocols, The 0Chain Consensus Protocol. Along with this, they also released their complete whitepaper which outlines all three products, marketing plans, and partnerships. The advanced speed gained by the use of this decentralized cloud storage consensus protocol allows Züs to provide storage enabled by the blockchain at speeds appropriate for everyday use. So let’s dive into the latest protocol:
Current protocols can take up to an hour, as in Bitcoin’s case. Newer technologies have been attempting to improve finalization times. 0Chain takes a new approach to provide a fast, flexible, and free platform for dApps through their unique proof-of-stake consensus protocol. By dividing the work among different groups, finalization time is improved by reducing network latency. This provides for faster access to stored data and quick transaction speeds.
Züs Cloud Network’s three key players:
Miners: run the consensus protocol and generate new transactions to the network.
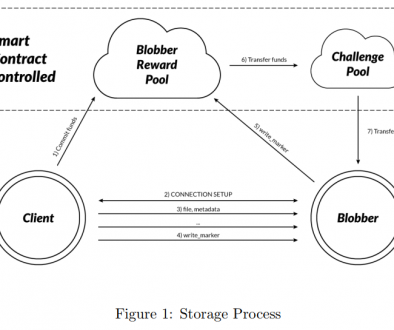
Blobbers: store data needed for dApps.
Sharders: store the blockchain history and respond to queries about the history
Clients, or those who hold ZCN, can become active within the network by acting as miners. All miners serve as notaries and implement the randomness beacon. They are further subdivided into those that act solely as miners and those that act as generators that extend the blockchain by proposing new transactions. In doing so, the network traffic and the time for messages to be sent are reduced. As mentioned above, sharders and blobbers also play specialized roles. This is a key component of 0Chain’s architecture. This also allows for more specialized machines such as a machine with high data storage capabilities for a blobber, but less computational power than a sharder may need.
0Chain aims to combat resistance from users having multiple accounts to flood the system by implementing a squared-staking approach. This means that miners and sharders are chosen via an algorithm that uses the square of the number of tokens they have staked (ZCN2). This encourages them to stake coins from a single account. This also places a greater risk of penalties if they fail to correctly run the protocol. While keeping in mind network latency, the 0Chain network is able to create faster finalization time because nodes can progress shortly after receiving messages. They do not need to wait until all messages have been delivered in a given round.

By utilizing this first-of-its-kind Cloud Storage Consensus Protocol, 0Chain implements the fastest blockchain network with finality times reaching as low as one second to enable seemingly instant transactions. By Chad Hanson on .